Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping of biomass: Synergistic mechanism of KOH and NH3
Recently, Master student Miss Yu-rou Wang supervised by Dr. Wei Chen and Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article entitled “Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping of biomass: Synergistic mechanism of KOH and NH3” in Renewable Energy.
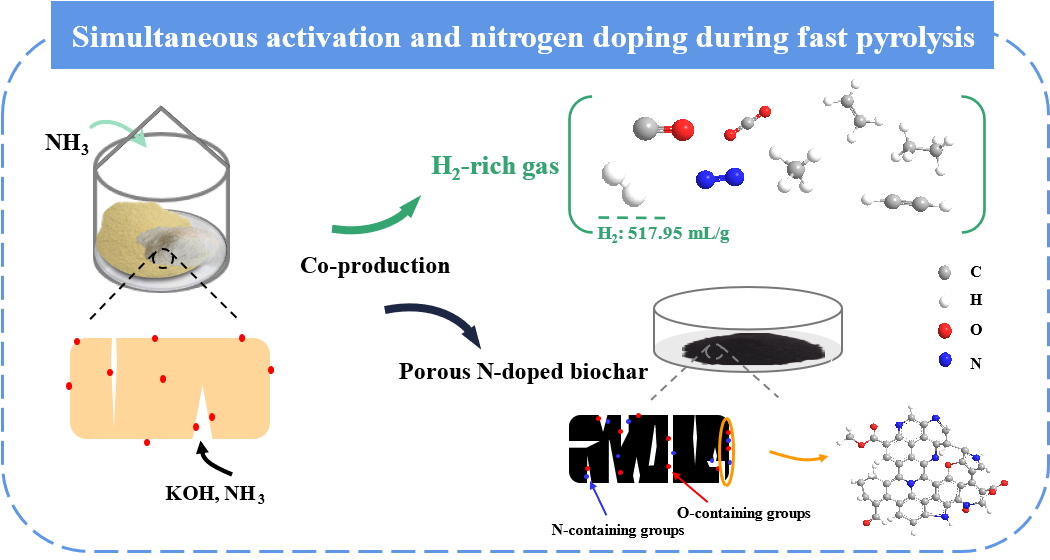
In this study, a method of simultaneous activation and nitrogen doping during biomass fast pyrolysis for co-production of porous N-doped biochar and H2-rich gas production was proposed. The effect of temperature on chemical interaction mechanism of KOH and NH3 was investigated at 500-800°C. Results showed that KOH and NH3 had a synergistic effect on pore development and nitrogen doping, and the specific surface area and nitrogen content reached maximum values of 2008.37 m2/g and 5.05 wt%, respectively. It may be due to that NH3 entered pores generating by KOH activation for further activation, and at the same time, excessive NH3 could convert new O-containing groups to N-containing groups for more effective nitrogen doping. What’s more, the H2 concentration and yield were up to 56.67 vol% and 517.95 mL/g, respectively. It indicates that the synchronization method of fast pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping is a promising approach, which is of great significance for the high-value utilization of biomass.
Related results were accepted in Renewable Energy:
Y. Wang, W. Guo, W. Chen*, G. Xu, G. Zhu, G. Xie, L. Xu, C. Dong, S. Gao, Y. Chen, H. Yang, H. Chen, Zhen Fang, Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping of biomass: Synergistic mechanism of KOH and NH3, Renewable Energy 229 (2024) 120777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.120777.
Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous activation and nitrogen doping during biomass fast pyrolysis 生物质快速热解过程中同步活化掺氮联产多孔掺氮炭和富氢气体
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
生物质同步热解-活化-掺氮联产多孔掺氮炭和富氢气体:KOH和NH3的协同机制
最近,硕士生王雨柔在陈伟副教授和方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Renewable Energy (Q1, IF = 8.7) 发表了一篇题为“Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping of biomass: Synergistic mechanism of KOH and NH3”的研究性论文。
本研究提出了一种在生物质快速热解过程中同步活化掺氮的方法,可以实现多孔掺氮生物炭和富氢气体的联产。探究了温度(500-800°C)对 KOH 和 NH3 化学协同作用的影响。结果表明,KOH 和 NH3 对孔隙发育和氮掺杂有协同促进作用,比表面积和氮含量分别达到最大值 2008.37 m2/g 和 5.05 wt%。这可能是由于 NH3 进入 KOH 活化产生的孔隙进一步活化,同时过量的 NH3 可以将新生成的含氧官能团转化为含氮官能团,从而实现更有效地掺氮。此外,热解气体中氢气浓度和产量可达到 56.67 vol% 和 517.95 mL/g。这表明,同步快速热解-活化-掺氮的方法前景广阔,对生物质的高值化利用具有重要意义。
结果发表在Renewable Energy:
Y. Wang, W. Guo, W. Chen*, G. Xu, G. Zhu, G. Xie, L. Xu, C. Dong, S. Gao, Y. Chen, H. Yang, H. Chen, Zhen Fang, Co-production of porous N-doped biochar and hydrogen-rich gas production from simultaneous pyrolysis-activation-nitrogen doping of biomass: Synergistic mechanism of KOH and NH3, Renewable Energy 229 (2024) 120777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.120777.