Lower temperature pretreatment of wheat straw for high production of fermentable sugars using ball-milling combined with deep eutectic solvent
Recently, PhD student Miss Li Wang supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article in Renewable Energy about pretreatment of ball-milling combined with deep eutectic solvent to enhance yield of fermentable sugar of wheat straw.
Mechanochemical pretreatment based on ball-milling (BM) and DES was designed to deconstruct wheat straw at moderate temperatures (50–60 ℃) for enzymatic hydrolysis. High glucose and xylose yield of 99.71 % and 92.77 % were achieved for 72 h enzymatic hydrolysis after BM assisted with choline chloride/oxalic acid (CO) treatment. This ascribes to the synergy of ball-milling and DES resulting in the loosening and collapse of lignocellulosic structures, leading to the selective removal and modification of hemicellulose and lignin. Relative saccharification activity of glucose and xylose was increased by 294.82 % and 658.41 % pretreated with BM and CO sequentially as compared with raw wheat straw, because of reduced crystallinity and increased of surface area and reducing-end concentration of pretreated wheat straw. Energy efficiency of ternary DES (CEO) system was 1.33 times that for the binary DES (CO) system during sequential treatment of BM and DES. Relative saccharification activity and energy consumption (or energy efficiency) was fitted as quadratic functions. This green and effective pretreatment method provides new insights for the lignocellulosic deconstruction.
Related results were published in Renewable Energy:
L Wang, CX Gong, JJ Guo, Zhen Fang*. Lower Temperature Pretreatment of Wheat Straw for High Production of Fermentable Sugars Using Ball-Milling Combined with Deep Eutectic Solvent, Renewable Energy (IF 9), 241 (2025), 122240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.122240
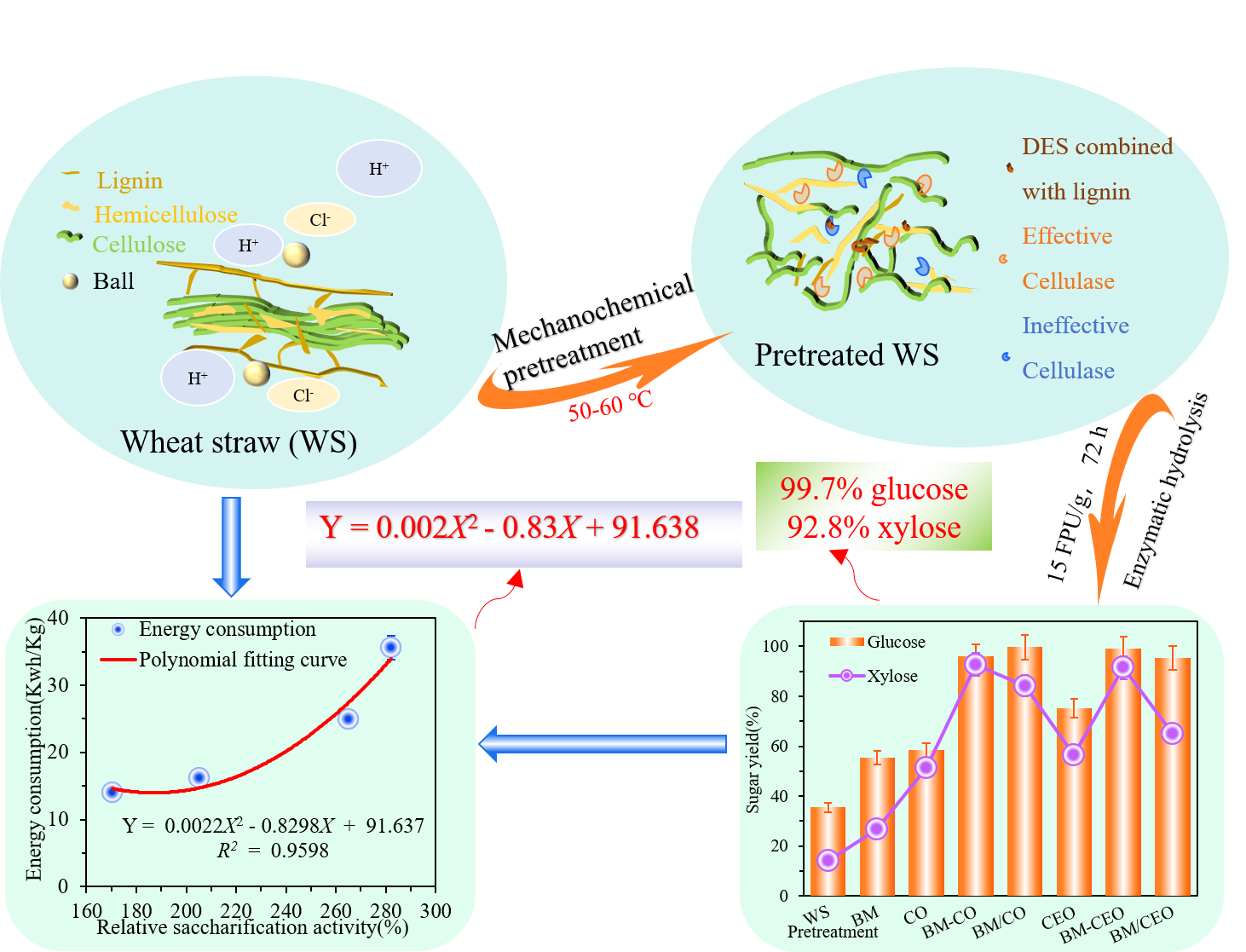
High sugar yield (99.7% glucose and 92.8% xylose) of wheat straw was achieved by ball-milling combined with deep eutectic solvent pretreatment at lower temperature. (采用球磨法结合低共熔溶剂在较低温度下预处理,小麦秸秆的葡萄糖得率达到99.7%,木糖得率为92.8%)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
球磨结合低共熔溶剂在温和温度下预处理小麦秸秆高产可发酵糖
近期,博士生王莉同学在方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Renewable Energy (Q1,IF 9)发表了一篇关于球磨结合低共熔溶剂在温和温度下预处理小麦秸秆高产可发酵糖的研究性论文。
设计了基于球磨和低共熔溶剂的机械化学预处理方法,在50-60°C的中等温度下对小麦秸秆进行预处理。球磨辅助氯化胆碱/草酸处理后,葡萄糖和木糖的产率在酶解72 h时分别达到99.71%和92.77%。这归因于球磨和DES的协同作用,导致木质纤维素结构松动和崩溃,半纤维素和木质素被选择性去除和改性。葡萄糖和木糖的相对糖化活性提高了294.82%和658.41%,这与小麦秸秆的结晶度降低,表面积和还原端浓度增加有关。在球磨和低共熔溶剂的顺序处理过程中,三元低共熔溶剂(氯化胆碱/乙二醇/草酸)体系的能量效率是二元低共熔溶剂(氯化胆碱/草酸)体系的1.33倍,同时建立了相对糖化活性与能量消耗(或能量效率)的二次函数关系。这种绿色有效的预处理方法为木质纤维素的解构提供了新的思路。
结果发表在Renewable Energy:
L Wang, CX Gong, JJ Guo, Zhen Fang*. Lower Temperature Pretreatment of Wheat Straw for High Production of Fermentable Sugars Using Ball-Milling Combined with Deep Eutectic Solvent, Renewable Energy (IF 9), 241 (2025), 122240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.122240