Enhancing xylose fermentation to maximize net energy gain of lime-pretreated wheat straw by delayed fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
Recently, master student Miss Wan-ying Qiu supervised by Dr. DC Dong and Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article in Biomass and Bioenergy (Q2, IF 5.8) about increasing net energy gain through delayed fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of wheat straw.
Delayed fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) of lime-pretreated wheat straw was carried out with a wild type yeast (i.e., Candida shehatae) to produce high titer ethanol. Calcium ions in lime-pretreated wheat straw were precipitated by pH controlling agent (i.e., sulfuric acid) to reduce inhibition of inorganic ions on yeast fermentation. It was found that ethanol concentration (∼35 g/L) did not increase as solid loading of substrate increased from 15 % to 20 % in batch SSF. However, in delayed fed-batch SSF, the feeding time of substrate (96 h) was postponed until after the inoculation time (18 h) resulting in a 74% reduction in residual xylose concentration and a 54.3% increase in ethanol concentration (54 g/L). Compared to batch SSF, separation energy of ethanol was decreased by 32.3% to 977.3 MJ/ton wheat straw in delayed fed-batch SSF, and net energy gain was increased by 20.1% to 3525.7 MJ/ton wheat straw.
Related results were published in Biomass and Bioenergy:
WY Qiu, CY Dong*, JJ Guo, B Xia, LJ Xu, Zhen Fang*. Enhancing xylose fermentation to maximize net energy gain of lime-pretreated wheat straw by delayed fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, Biomass and Bioenergy (IF 5.8), 198 (2025), 107865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2025.107865
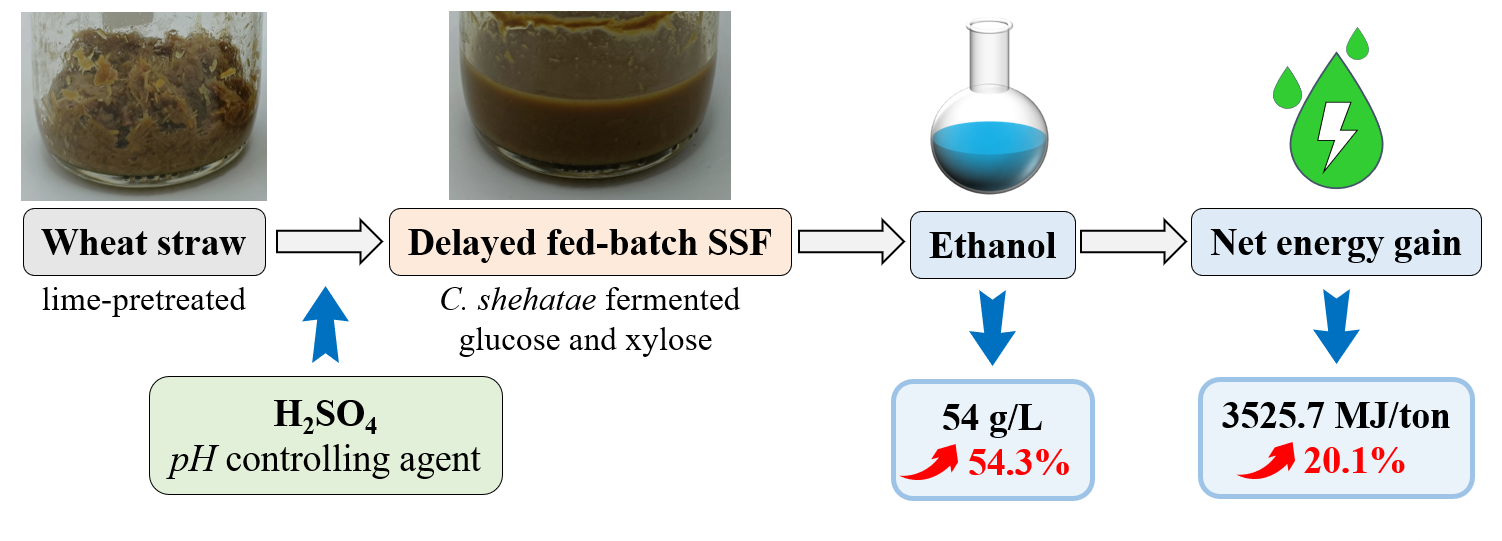
Ethanol concentration was increased by 54.3% by xylose fermentation in delayed fed-batch SSF. (采用延迟补料式同步糖化发酵,发酵木糖使乙醇浓度提高了54.3%)
延迟补料式同步糖化发酵氢氧化钙预处理小麦秸秆提高乙醇产量
近期,硕士生邱婉莹同学在董澄宇博士和方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Biomass and Bioenergy(Q2, IF 5.8)发表了一篇关于通过延迟补料式同步糖化发酵小麦秸秆提高乙醇产量的研究性论文。
利用休哈塔假丝酵母(Candida shehatae)对氢氧化钙预处理小麦秸秆进行延迟补料式同步糖化发酵,以生产高浓度乙醇。使用硫酸作为pH调节剂沉淀氢氧化钙预处理小麦秸秆中的钙离子,减少无机离子对酵母发酵的抑制作用。在分批补料式同步糖化发酵中,底物固载量从15%提高至20%时,乙醇浓度均约为35 g/L,并未显著增加。然而,在延迟补料式同步糖化发酵中,补料时间(96 h)推迟至接种时间(18 h)之后,使木糖残留浓度降低74%,乙醇浓度增加54.3%(达到54 g/L)。与分批补料式同步糖化发酵相比,延迟补料式同步糖化发酵中乙醇的蒸馏耗能为977.3 MJ,降低32.3%,且每吨小麦秸秆的净能量收益达到3525.7 MJ,增加20.1%。
结果发表在Biomass and Bioenergy:
WY Qiu, CY Dong*, JJ Guo, B Xia, LJ Xu, Zhen Fang*. Enhancing xylose fermentation to maximize net energy gain of lime-pretreated wheat straw by delayed fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, Biomass and Bioenergy (IF 5.8), 198 (2025), 107865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2025.107865